What is pH?
Scientist don't have a clue what pH stands for... pH can be the Power or the Potential Hydrogen in a aqueous solution.
The more hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution the more acidic it is.
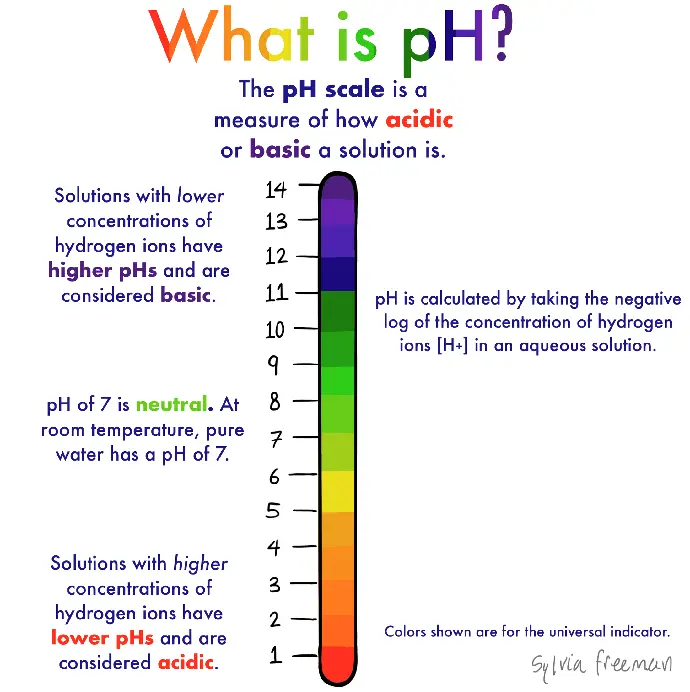
What's pH?
The term pH measures how acidic or basic an aqueous solution of water is. A pH scale uses a logarithmic system and ranges from 1 – 14 with the lowest number representing the more acidic a solution and the highest number 14 being the more alkaline.
A pH of 1 – 6.9 is acidic, and basic is a pH of 7.1 – 14 with pH 7 being neutral. The logarithmic system multiplies by 10 between sequential pH numbers increasing a pH of 8 to a pH of 9 making the solution of water (100 times) more alkaline than the last number.
That’s a huge difference when our blood ranges between a pH of 7.35 to 7.45 and any changes under or below those numbers can put the body into shock or death. For instance failure of the lungs and kidneys ability to regulate the raising of the pH over 7.45 causes a condition called alkalosis and if the pH drops below 7.35 its called acidosis.
Alkalinity / Buffering
Alkalinity is a base solution of dissolved alkali salts that posses the ability to buffer acidity. But How? Alkaline salts are naturally produced and grouped within the first two categories on the periodic table Group 1 Alkali Metals and Group 2a Alkaline Earth Metals. Alkali Metals are lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, francium and all are reactive with water to form alkalies which are strong bases with the ability to buffer and neutralize acids. Alkaline Earth Metals are oxides from metal compounds joined together with oxygen creating natural salts that consists of beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and radium.
Understanding Alkalinity Similarity
Our oceans has to have a salty consistency to consistently buffer the acidic waste of all living organisms of the earth and our human bodies are not far from comparison.
The ability to neutralize acidic conditions within the aqueous environment helps to prevent possible health risk to the organisms that may occur due to the change in pH. Every organism has an environment that is optimum for its living conditions. The environment dictates the nature of the cell. Like pH for fish in the ocean or in a fish tank our cells are the direct comparison within our human bodies. For a fish its a little more simple but much of the same basics because it's largely based on the denaturing of the cellular membrane which is the movement of water inside the fish and out the fish/organism body.
A change in pH can cause a multitude of problems for us as humans because it is connected to so many trigger points from our skin to our hormones.
The human body runs on a series of buffering systems but the lungs and the kidney's regulate the balance of blood pH. Our duty is to provide the daily requirements of hydration through multiple avenues or streams into organs of tissues to cells to achieve optimum hydration. This takes place through mouth orally from natural spring water which is called free moving water and food with high water content. The moisture in the air helps the lungs to remain hydrated and the absorption of salt water through our skin helps to regulate the balance of water and acidity in the body by assisting with the lubrication of joints and muscles.
Those systems establish the regulations of acid vs alkalinity within the body. Alkalinity is determined in the concentration of minerals found in a solution such as (bicarbonates, carbonates, and hydroxides) with the ability to buffer acidic conditions. This is why minerals salts are so important because it aids the buffering systems to prevent them from pulling minerals such as calcium thats deposited in the bones into the bloodstream.
Calcium is removed from the bones to neutralize acidic overload in the blood. This is regulated by the parathyroid hormone (PTC) which raises the calcium levels in the blood. 99% of calcium is found in the bones and the remaining 1% is in the blood, muscles and tissues.
Did You Know?
Bone spurs are calcium deposits that settle on the bone. This can happen once calcium is removed from the bone to buffer an acidic condition. Once neutralized calcium can't be deposited back into the bone so it settles on the bone as a bone spur.
Chemical Reaction / pH Drops vs pH Strips

The Same but Different
The pH measurement is a critical parameter in various fields such as chemistry, biology, agriculture, and environmental science.
Two common methods used to measure pH are pH strips and pH drops.
But the differences between pH strips and pH drops, including how they work, and their level of accuracy can be night and day depending on the information your looking for.
The pH strips are widely used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The alkalinity is determined by the mineral content within the solution. They are available with varying levels of accuracy and can cover different ranges of the pH scale. Typically, pH drops offer higher accuracy and cover a larger range of the pH 1-14 scale. For instance, some pH strips may only cover half of the pH scale, limiting their use in certain scenarios.
The pH strips are small paper strips impregnated with a pH-sensitive dye that changes color in response to the solution's pH level. The dye on the strip interacts with the hydrogen ions (H+) present in the solution.
pH Drops consist of a specific chemical compound that reacts with the hydrogen ions in the sample, causing a color change. The number of drops required to achieve the desired color change corresponds to the pH level, which can be determined by consulting the reference chart.
pH Testing strips vs testing drops
The pH strips tells the story of its buffering capacity of alkalinity which is the amount of total dissolved solids (TDS) of minerals present. Hydrogen ions represent how acidic a solution is and the more free hydrogen ions the more acidic the solution of water.
Having a high pH number means nothing without the minerals to go with it. It is the same as eating food with no nutritional value. Empty calories serve no purpose for the human body. The objective is to replace whats lost and prevent our body from depleting the reserves stored in the bones.
Electrolysis is the splitting of water molecules. Wen water (H2O) separates from one another Hydrogen (H2) and Oxygen (O) no longer share an electron .
Molarity is calculated by dividing the moles of liter of water used in a solution. The molar concentration is the amount of moles in a solute (minerals) or chemical species in a volume of water. The molar concentration is a determining factor for both tests. The strips check the amount of solute in water and identify its ability to resists changes. The pH drops are shaped by the chemical reaction of the solutes taking place within the solution.
The alkalinity represents the amount of mineral salts or (TDS) within the water and its ability to buffer acidic changes of pH. The pH drops chemical reaction that takes place within the water in order to decide how acidic it is determined by the number of drops it takes to raise the pH level to the desired color of the indicator.
Image Source: by Sylvia Freeman and Deena Hauze
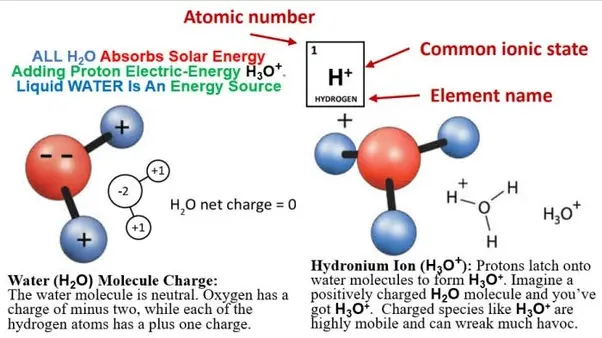
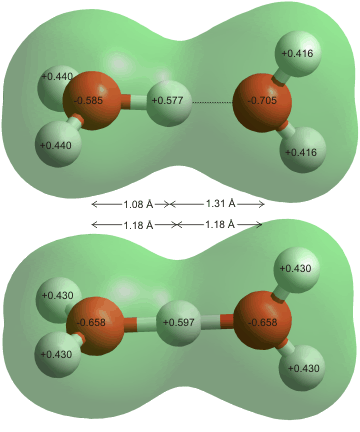
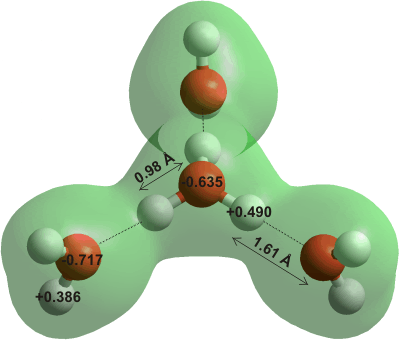
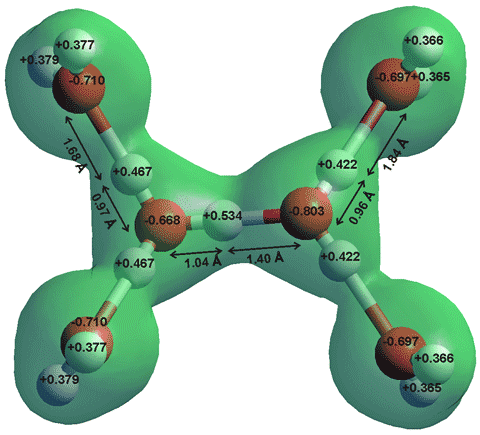
The constant movement of water molecules can change the pH of water... but how? Molecules of water are bonded to one another through hydrogen bonds. A hydrogen bond is a type of weak chemical bond with an Intermolecular Force (IMF) that creates a special type of dipole dipole attraction when the hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as oxygen exists in the proximity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons. This means that the hydrogen atom (H+) of one molecule of water will bond to the oxygen (O-) side of different water molecule.
Often within this action of (IMF) the movement of water molecules may lose a hydrogen atom moving around or to the oxygen side of different water molecule creating a hydronium ion (H3O+) and a hydroxide ion (OH-) pH is the measurement of the quantity of hydrogen ions or positively charged molecules within an aqueous solution.

How does pH balance affect your body?
The pH balance of substances such as your bodily fluids and organs can affect your digestion, hormones, metabolism, and overall body function.
Value your pH
Don't drink water with your meals!
Drinking water while eating will raise the pH of the stomach acid neutralizing the antimicrobial effects that the acidic low pH has to offer for digestion keeping a clean healthy gut.
Begin with digestion phase in the stomach your pH is meant to be acidic very low